Ancient Greece can be credited with many inventions and discoveries, although many of these have been developed and adapted by subsequent generations. The ancient Greeks’ findings in the areas of astronomy, geography, and mathematics made them pioneers in the field of science. Here is a list of the top 5 inventions and discoveries of ancient Greece that are still used today.
Olympics
The modern Olympics are one of the greatest sporting spectacles of the modern age. But when Pierre de Coubertin, the founder of the international Olympic committee, started the first modern Olympics in 1896, he was inspired by the ancient Olympics that were held in Greece more than 2,700 years ago. According to historical records, the first ancient Olympic Games can be traced back to 776 BC. They were dedicated to the Olympian gods and were staged on the plains of Olympia.

Earliest Practice of Medicine
The ancient world did not fare too well when it came to the curing of disease. Back then, diseases were supposed to be the gods’ way of punishing humans and all possible remedies were surrounded by superstition.
That all changed when Hippocrates of Cos started to collect data and conduct experiments to show that disease was a natural process; that the signs and symptoms of a disease were caused by the natural reactions of the body to the disease process.

Born in 460 BC, Hippocrates was an ancient Greek physician of the Classical age and was considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He was referred to as the father of Western medicine in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field and was the founder of the Hippocratic School of Medicine.
The most famous of his contributions is the Hippocratic Oath, which bears his name. It was this document that first proposed an ethical standard among doctors. It covers many important concepts which are still used today such as doctor–patient confidentiality.

Cartography
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. It has played an important role in travel and navigation since ancient times. Even though the earliest known evidence of cartography points towards ancient Babylon as early as the ninth century BC, the Greeks took what they had at their disposal and brought cartography into a new light. Anaximander was one of the first pioneer cartographers to create a map of the world. Born between 611 and 610 BC, he made important contributions to the science of astronomy and geography.

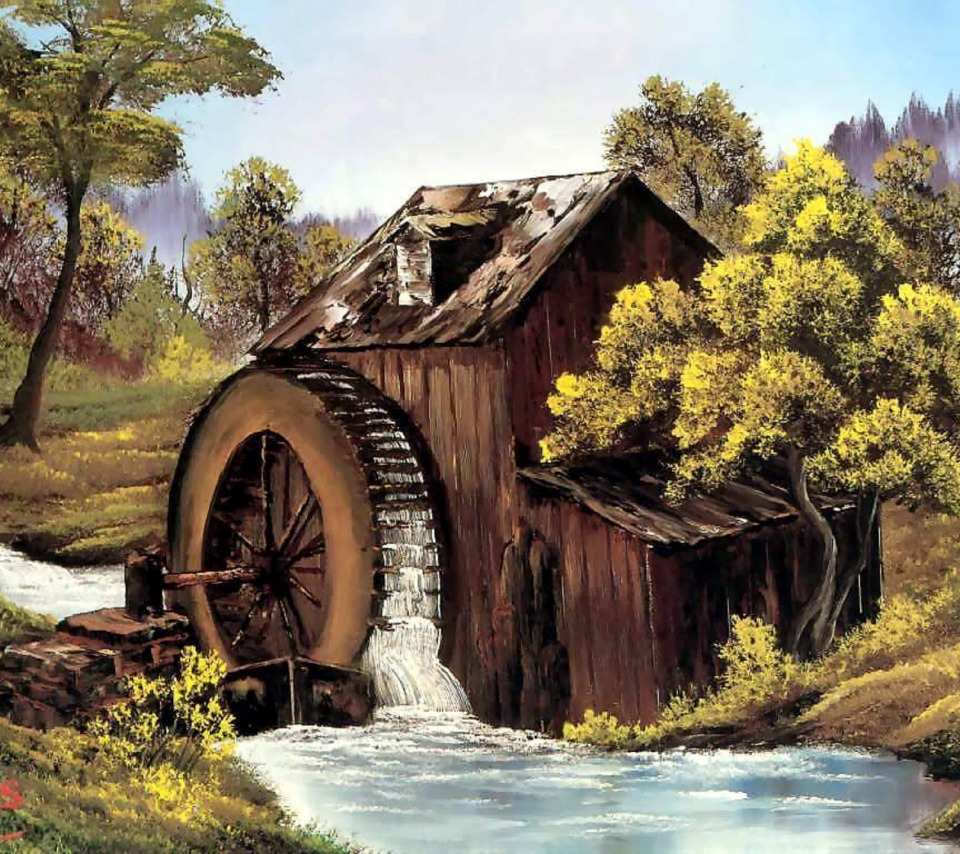
The Water Mill
This useful invention takes its origins from the earliest known Perachora wheel, created way back in the third century BC in Greece, most likely invented by the contemporary Greek engineer Philo of Byzantium. Earlier, the portions of the mechanical treatise on this particular water mill written by Philo himself were regarded to have Arab origination. However, recent research by British historian M.J.T. Lewis has proved that the water mill was an ancient Greek invention.

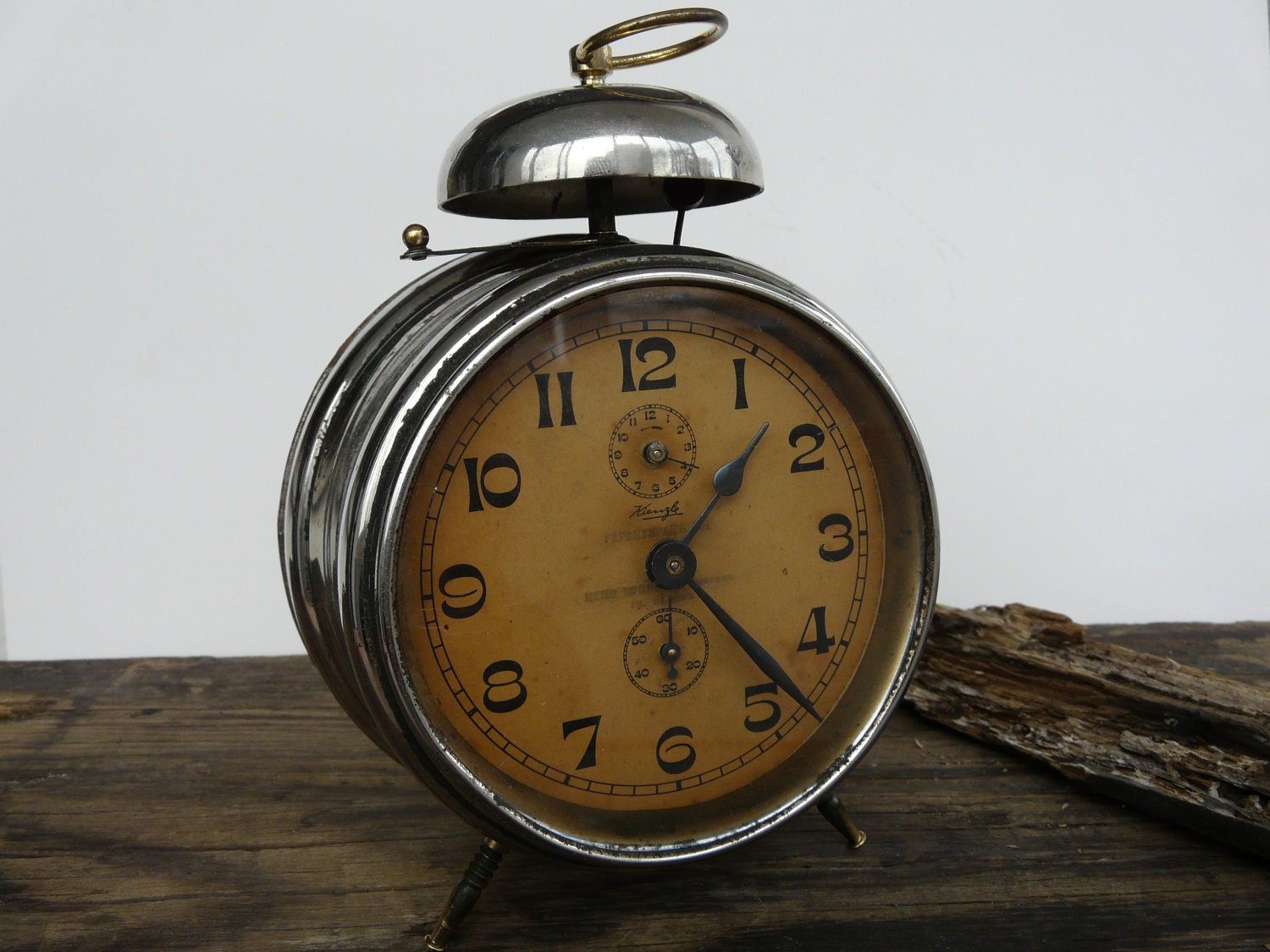
The Alarm Clock
One of the most commonly used gadgets these days is the alarm clock, and it too had its origins in ancient Greece. Over time, the alarm clock has undergone a number of changes and improvements from the mechanical alarm to modern gadgets like cell phones, which come with an inbuilt alarm. The ancient Greek philosopher Plato (428–348 BC) was said to possess a large water clock with an unspecified alarm signal similar to the sound of a water organ. He used it at night, possibly for signaling the beginning of his lectures at dawn.

Modern Philosophy
Before the age of ancient Greece, the world did not see philosophy as we see it today. It was more shrouded in superstition and magic than it ever would be. But the Greeks approached philosophy from a different direction. They developed philosophy as a way of understanding the world around them, without resorting to religion, myth, or magic. In fact the early Greek philosophers were also scientists who observed and studied the known world, the earth, seas, mountains, solar system, planetary motion, and astral phenomena.